In essence, understanding deposits in transit is crucial for anyone involved in the financial aspects of a business. They must track these deposits meticulously, ensuring that once the bank has processed them, the books balance with precision. This adjustment is necessary to make the bank’s records align with the company’s cash balance.
Understanding Deposits in Transit and Their Role in Bank Reconciliation
As deposits are received by the bank, they are initially recorded as deposits in transit on the reconciliation statement, reflecting the deposit amount. A deposit in transit is cash you’ve logged in your company’s books but that hasn’t made it to the bank statement yet. By tracking deposits in transit accurately, businesses can better predict their actual cash availability and avoid cash flow issues. This can impact cash flow management, especially if a business relies on timely deposits for day-to-day operations.
For example, if a company deposits a large check but it hasn’t cleared, the company’s cash on hand is lower than expected, potentially affecting its ability to cover expenses. While deposits in transit are technically cash that belongs to the business, the funds are not yet available for immediate use. In this case, there is no deposit in transit, since the bank’s records are updated in advance of the records maintained by the company. When a company uses a bank lockbox, payments go from customers straight to the bank, at which point the bank records the deposits and then notifies the company of the receipts. If this occurs at month-end, the deposit will not appear in the bank statement issued by the bank, and so becomes a reconciling item in the bank reconciliation prepared by the entity. However, the bank statement will report the $4,600 as a deposit on Monday, July 1, when the bank processes the items from its night depository.
Deposit in Transit: Deposit in Transit: Bridging the Gap in Your Bank Reconciliation Process
The challenge lies in the timing; deposits in transit are funds that have been recorded in a company’s books but not yet reflected in its bank statement. The timing of recognizing deposits in transit is a critical factor in the bank reconciliation process. The company must ensure that this deposit is accounted for in the reconciliation process to maintain accurate financial records. Understanding and managing deposits in transit is a balancing act that requires coordination between a business’s accounting practices and the bank’s processing protocols. These deposits represent funds that have been received but not yet recorded by the bank, creating a discrepancy between the company’s cash records and the bank statement. They may use cut-off tests around the year-end to verify that deposits in transit are reflected correctly in both the bank statement and the company’s cash records.
Ensuring accuracy in financial reporting is paramount for the credibility and reliability of any business’s financial statements. This allowed them to leverage the expertise and advanced technology of the service provider, resulting in more efficient and accurate reconciliations. The system automatically matched deposits using algorithms, flagging any discrepancies for review.
- And deposits in transit are a natural consequence of that.
- In the realm of global business, the ability to communicate with precision is not merely a…
- Look for deposits recorded in the company’s records that are not present on the bank statement.
- Accounting software also has options for checking differences between intercompany transactions and bank statements, for example.
- Also, the bank should mail the statement directly to the person who reconciles the bank account each month.
- This temporal gap is the breeding ground for deposits in transit.
Identifying Deposit in Transit in Your Financial Statements
For deposits still pending, you can physically mark the relevant slips or add comments to digital transaction logs. Whether it’s an honest mistake or something more malicious, missing deposits can slip through the cracks. When your books and your bank statement don’t match, you could make decisions based on incomplete information.
That is, funds you’ve recorded but the bank hasn’t processed yet. It’s necessary because your records don’t always match your bank statement. Bank reconciliation is a standard process to help you determine how much money your business can work with at any moment.
C) They track deposits separately and link up with bank accounts The computerization of deposit in transit processing minimizes human interface and helps in efficient and accurate recording of daily transactions and monies in transit. Accounting software also has options for checking differences between intercompany transactions and bank statements, for example. Being consistent while keeping records is the first step towards effective tracking of deposits in transit.
The payment is said to be in transit from the account holder to the payee. Transits can be described as the payments that occur between parties of different banks. A guide to attorney billable hours charts and how to calculate time increments Get our latest business advice delivered directly to your inbox.
For example, if you deposit checks at the end of the business day, ensure that these amounts are logged and cross-referenced with bank receipts. In the intricate dance of bank reconciliation, deposits in transit play a pivotal role. By carefully managing and accounting for these timing differences, companies can ensure more accurate financial reporting and make better-informed business decisions. The timing of deposits in transit is more than just a clerical concern; it has real implications for the financial health and operational efficiency of a business. Meanwhile, for business owners, understanding deposits in transit can provide insights into the timing of cash receipts and can help in managing the working capital more effectively. It records the deposit on Friday’s ledger, but the bank will only process it on Monday, making it a deposit in transit over the weekend.
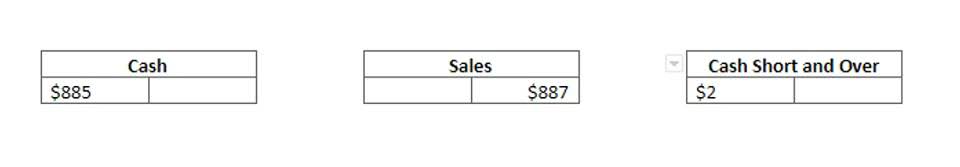
Each has a vital role, and understanding their parts is key to ensuring a standing ovation (or, you know, financially accurate books!). Also, the bank should mail the statement directly to the person who reconciles the bank account each month. For example, a $47 check may be recorded as $74.
Today we’ll look at one of the more common reasons for such mismatches—deposits in transit. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement using the above information. Company A’s bank statement dated Dec 31, 2011 shows a balance of $24,594.72. The bank processes the deposit later.
Example of Deposit in Transit
From the bank’s standpoint, deposits in transit are not yet on their books, so they do not impact the bank’s balance sheet until they are processed. Deposits in transit are an essential element of the bank reconciliation process, representing funds that have been received and recorded by a business but not yet by its bank. For businesses using accrual basis accounting, reconciliation becomes even more critical to distinguish between recorded transactions and actual cash movements. The process protects your business by catching errors, preventing fraud, and ensuring your financial records accurately reflect your cash position. Bank reconciliation is much easier when you understand the language used in your bank statements and accounting records.
Deposit in Transit: In Transit but Not Lost: Navigating Deposit Reconciliations
These are the key concepts you need to understand to accurately answer the question. High-volume businesses may reconcile weekly or daily. In very small businesses, the owner often handles both roles. Use tools like the ROI calculator alongside reconciliation data. Many businesses use an Excel how to calculate amortization template for easy customization.
This is important for financial accounting because it keeps track of timing differences that may cause difficulty in reconciling the company’s cash balance to its monthly bank statements. The deposits in transit are one of the key components of bank reconciliation that helps in how a business organizes its records to reflect its real cash position. The term “deposit in transit” is related to the cheques or non-cash payments that the company accepted and recorded in the accounting system but not yet processed by the bank. A deposit in transit typically clears within one to three business days, depending on the bank’s processing time and the type of deposit (e.g., check, cash, electronic).
The concept of deposit in transit is one of the important steps towards maintaining accuracy in record keeping. Delays may occur if the deposit is made late in the day, on weekends, or on holidays. This situation can arise when a company’s accountant is away on vacation or is otherwise occupied. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- Mark items appearing in both records as cleared using proper journal entry accounting procedures.
- Timing gaps between your records and bank processes are a standard part of running a business.
- This also helps in the early detection of any discrepancies due to fraud or accounting mistakes.
- These tools can match deposits recorded by the business with those recorded by the bank, flagging any discrepancies for review.
- This is much more than just a quick check—it’s a key process that keeps your records accurate.
Meanwhile, auditors appreciate the traceability and transparency that technology brings to the table, making it easier to verify the integrity of financial records. By updating their banking details and training their staff on the importance of double-checking these details, they can overcome this challenge. Deposits in transit can often be a source of frustration for businesses and financial teams. This could involve checking the bank’s online platform for the most recent transactions.
This is much more than just a quick check—it’s a key process that keeps your records accurate. This timing gap means your books and your bank balance don’t match—but only for a short time. This article breaks down selling on etsy andyour taxes what deposits in transit are, how they work, and why they matter to your business.
Deposits in transit do not affect the account balance, as they are not yet considered part of the account’s available balance. These deposits are often referred to as “uncleared” or “unposted” deposits. These programs make tracking easier and faster by connecting to bank records and recording automatically. Avoid these screw-ups by having checks in place and training your team to keep things consistent. You can end up with double entries, missed deposits, or wrong amounts. The bank might pull that amount from your account to fix any mess-up.
This ensures that the company’s accounting records accurately reflect the available funds in the bank. Weekends and holidays are also a factor, as banks typically don’t process deposits on these days, creating a delay in posting them to the account. Deposits in transit occur primarily due to timing differences between when a company records a deposit and when the bank processes it.